目录
😀
CVE-2019-13288漏洞分析
简述
在 Xpdf 4.01.01 中 Parser.cc 中的 Parser::getObj() 函数可能会通过精心设计的文件导致无限递归 远程攻击者可以利用它进行 DoS 攻击
环境配置
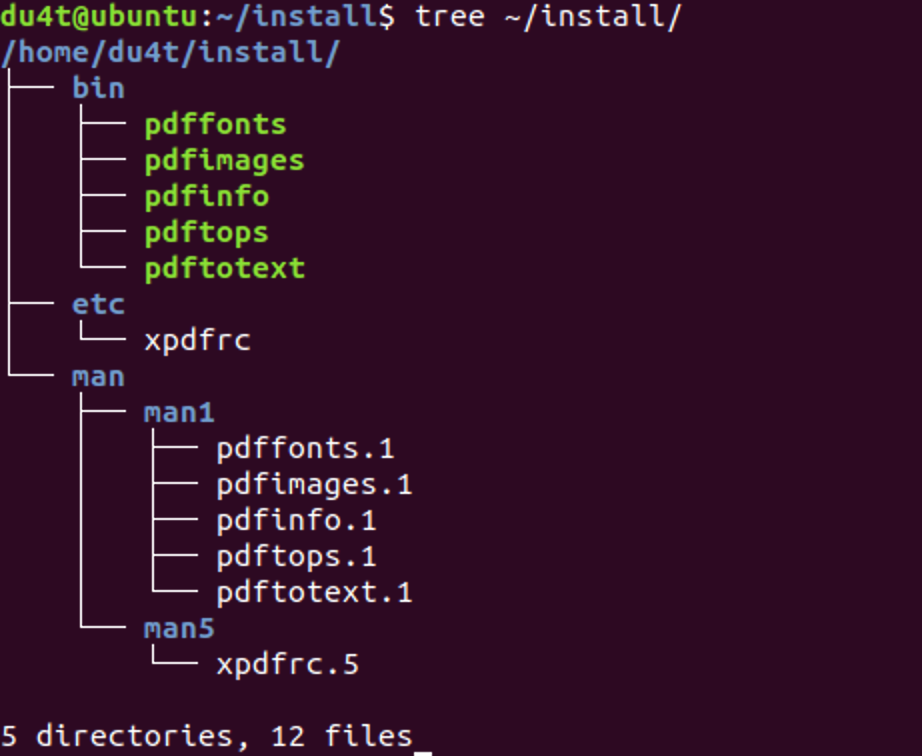
Xpdf版本选用3.02
下载对应版本Xpdf并解压
bash$ wget https://dl.xpdfreader.com/old/xpdf-3.02.tar.gz $ tar -xvzf xpdf-3.02.tar.gz

创建临时文件夹
bash$ mkdir ~/install/
编译Xpdf
bash$ ./configure --prefix="$HOME/install/"
$ make
$ make install
下载测试样例
bash$ mkdir example & cd example
$ wget https://github.com/mozilla/pdf.js-sample-files/raw/master/helloworld.pdf
$ wget http://www.africau.edu/images/default/sample.pdf
$ wget https://www.melbpc.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/small-example-pdf-file.pdf
AFL基础依赖配置
bash$ sudo apt-get install -y build-essential python3-dev automake git flex bison libglib2.0-dev libpixman-1-dev python3-setuptools
$ sudo apt-get install -y lld-11 llvm-11 llvm-11-dev clang-11 || sudo apt-get install -y lld llvm llvm-dev clang
$ sudo apt-get install -y gcc-$(gcc --version|head -n1|sed 's/.* //'|sed 's/\..*//')-plugin-dev libstdc++-$(gcc --version|head -n1|sed 's/.* //'|sed 's/\..*//')-dev
编译AFL++
bash$ git clone https://github.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus & cd ./AFLplusplus
$ export LLVM_CONFIG="llvm-config-11"
$ make
$ sudo make install

使用afl-clang-fast重新编译Xpdf
bash$ cp -r ./AFLplusplus ~/
$ cd ./xpdf-3.02
$ make clean
$ export LLVM_CONFIG="llvm-config-11"
$ CC=$HOME/AFLplusplus/afl-clang-fast CXX=$HOME/AFLplusplus/afl-clang-fast++ ./configure --prefix="$HOME/install/"
$ make
$ make install
漏洞分析
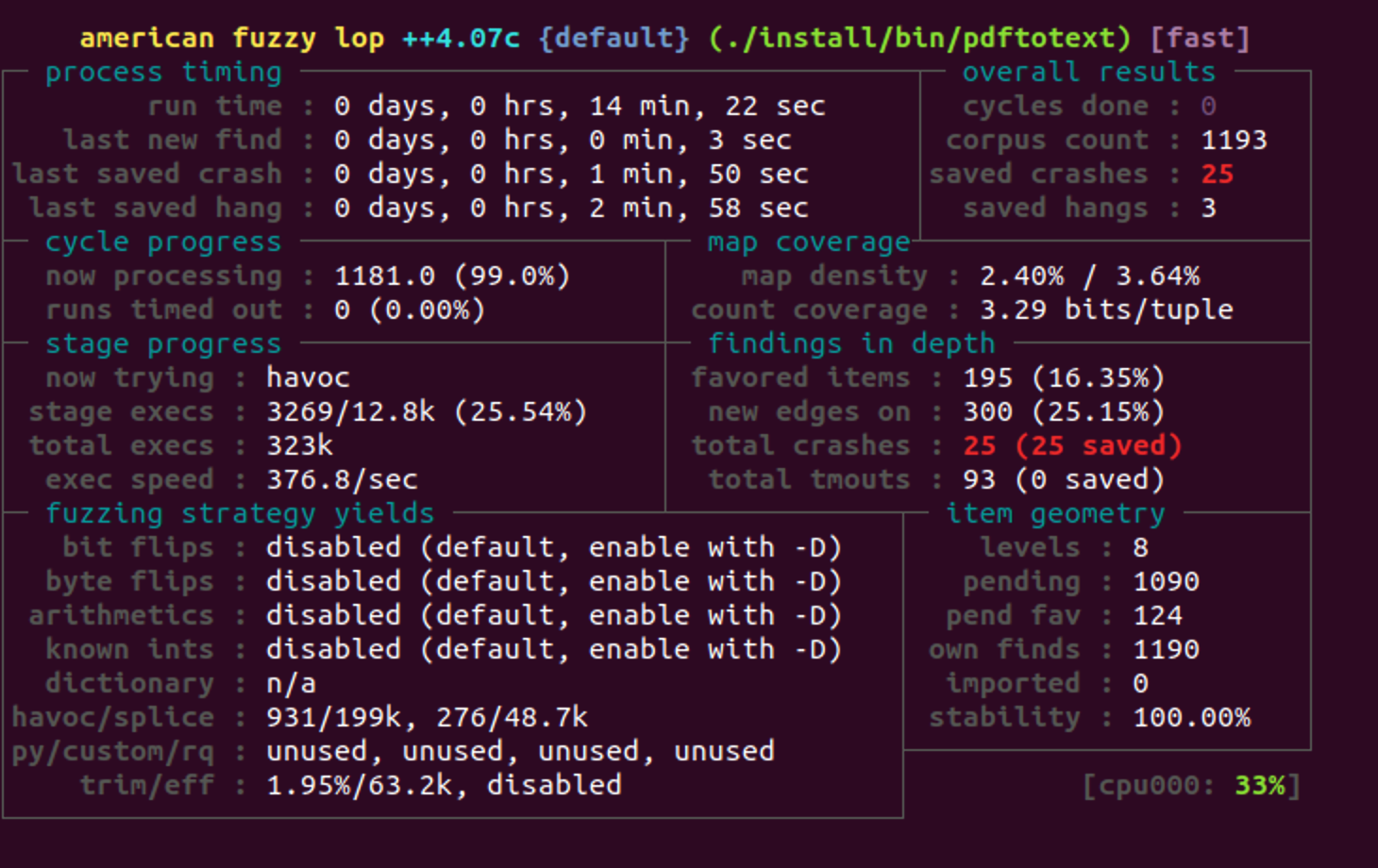
使用AFL对pdftotext进行FUZZ
bash$ afl-fuzz -i ./example/ -o ./out/ -s 123 -- ./install/bin/pdftotext @@ ./output/
玩了会手机 发现有25个crash
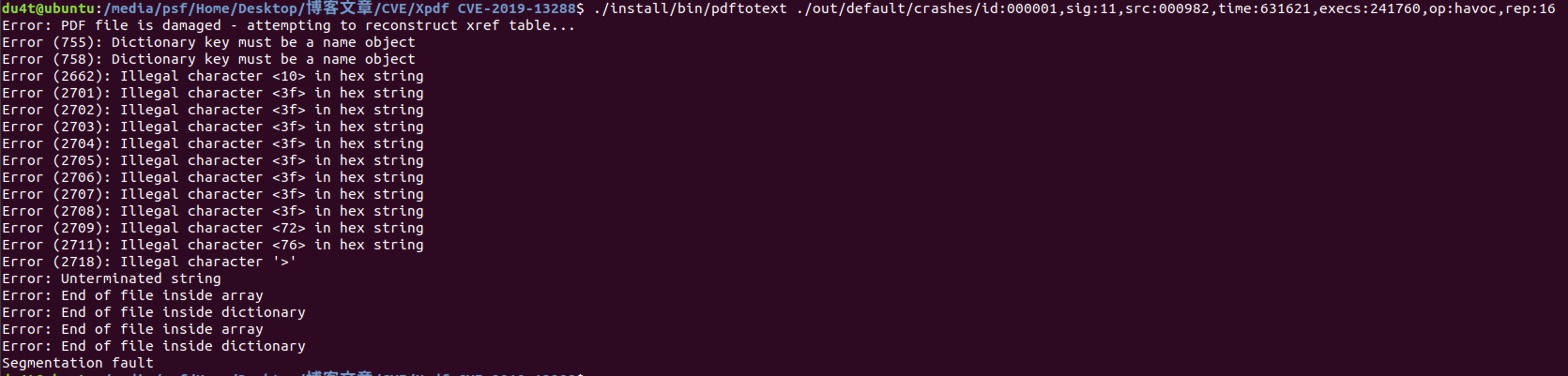
随便找一个crash样例测试一下 可以看到确实导致pdftotext段错误从而崩溃
bash$ ./install/bin/pdftotext ./out/default/crashes/id:000001,sig:11,src:000982,time:631621,execs:241760,op:havoc,rep:16
使用GDB载入测试

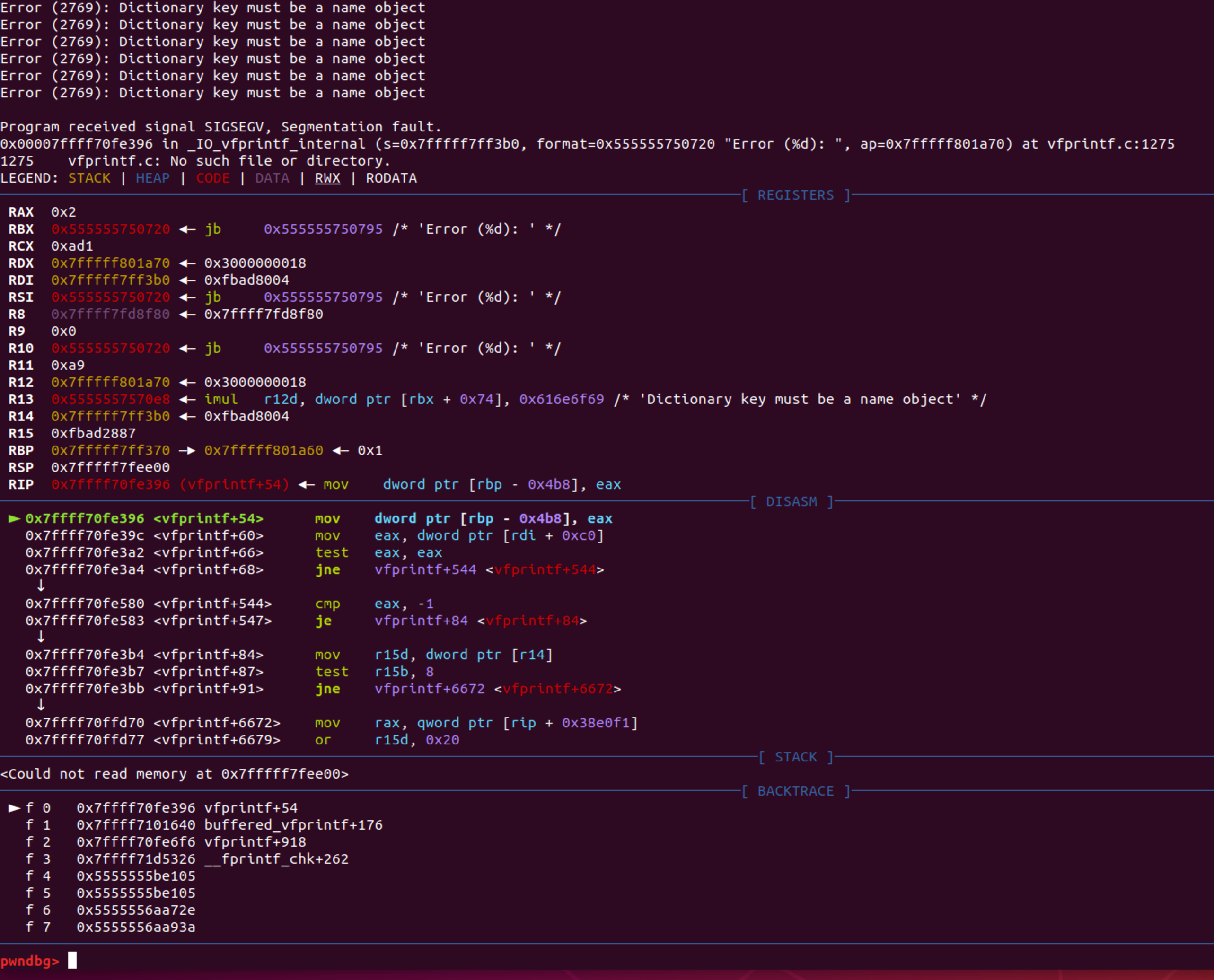
既然漏洞文档说了是无限递归问题 那么就使用bt指令查看下栈帧 发现确实是无限递归调用 那么现在问题就是无线递归的起始点在哪
通过翻看栈帧调用其实也能基本确定 很明显#58137 - #58131是一个循环节 即dictLookup() -> fetch() -> getObj() -> getObj() -> getObj() -> getObj() -> makeStream()
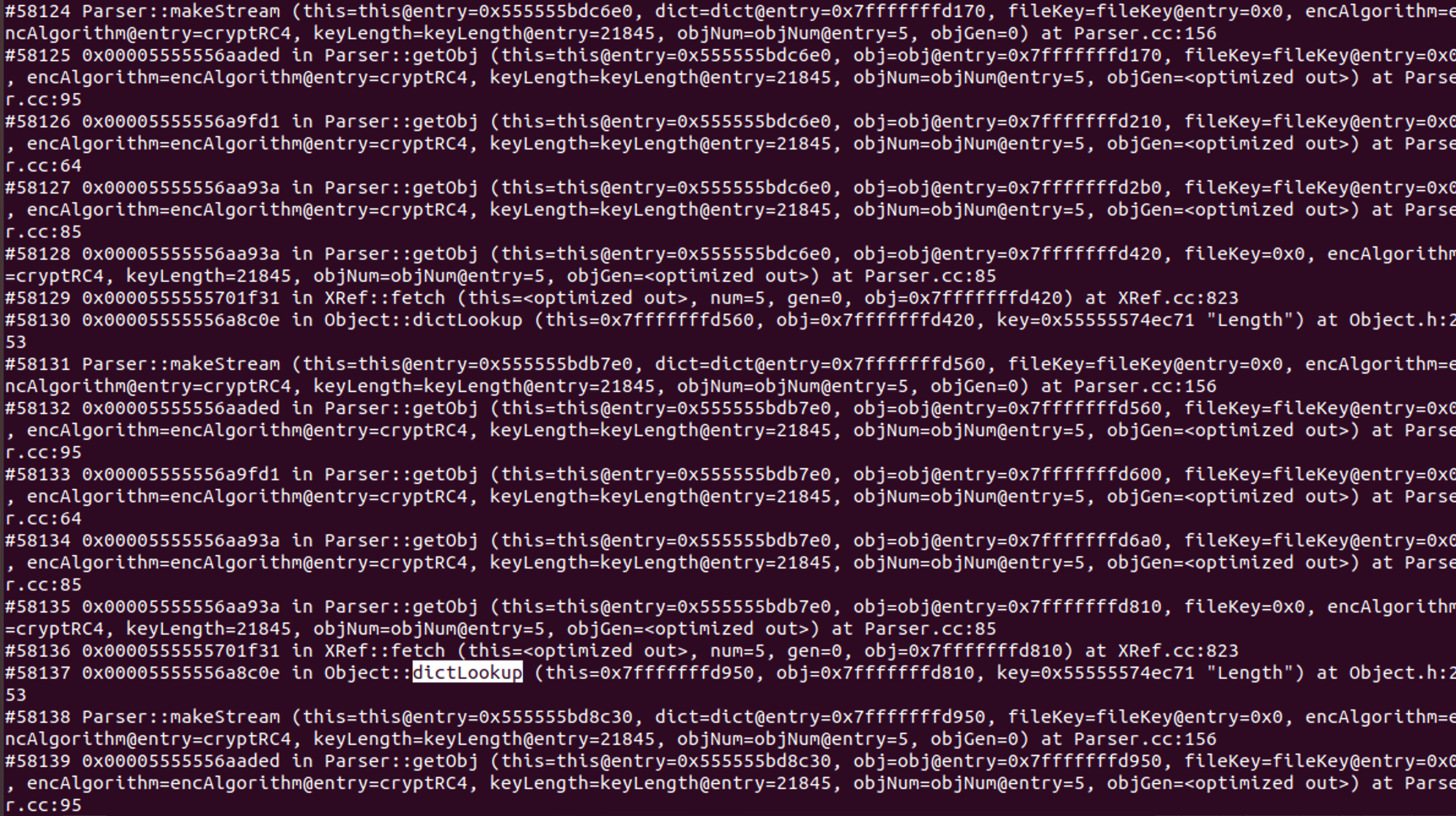
其次 通过分析最初始的栈帧调用 很明显第一次调用是没有问题的 关键就是在于makeStream() -> dictLookup()这一步
可以从源码级来审视一下调用 在pdftotext.cc:151新建了一个PDFDoc对象 且此时的参数fileName类型为GString
c// xpdf/pdftotext.cc
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
...
// open PDF file
if (ownerPassword[0] != '\001') {
ownerPW = new GString(ownerPassword);
} else {
ownerPW = NULL;
}
if (userPassword[0] != '\001') {
userPW = new GString(userPassword);
} else {
userPW = NULL;
}
doc = new PDFDoc(fileName, ownerPW, userPW);
...
}
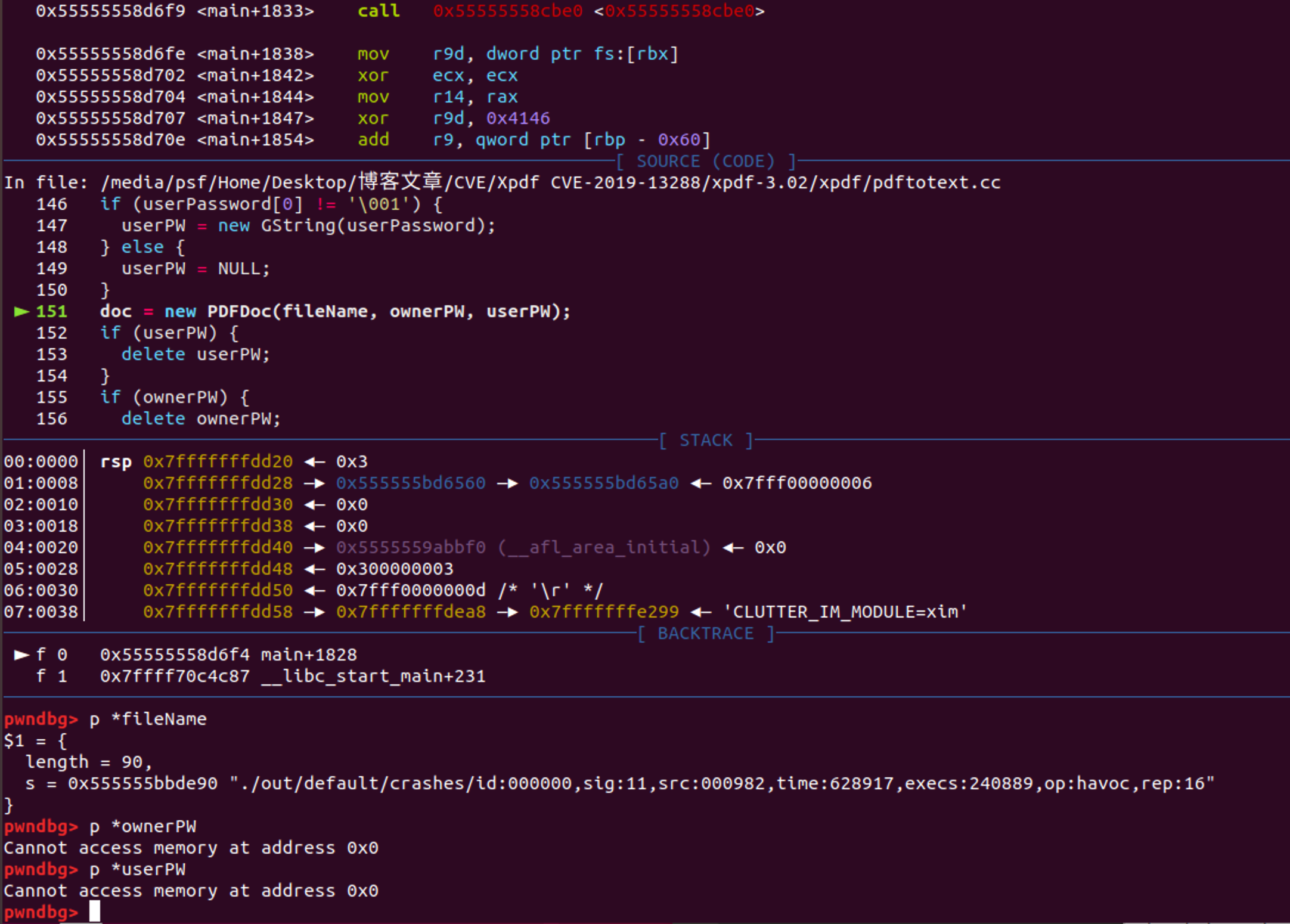
根据参数类型选择对应的PDFDoc 整体逻辑很简单就是打开文件 然后创建文件流 最后调用PDFDoc::setup() 因为我们在最初始的时候没有传入密码相关的参数 所以此时的ownerPassword和userPassword按道理来说仍然指向0x0
c++// xpdf/PDFDoc.cc
PDFDoc::PDFDoc(GString *fileNameA, GString *ownerPassword,
GString *userPassword, void *guiDataA) {
Object obj;
GString *fileName1, *fileName2;
ok = gFalse;
errCode = errNone;
guiData = guiDataA;
file = NULL;
str = NULL;
xref = NULL;
catalog = NULL;
fileName = fileNameA;
fileName1 = fileName;
// try to open file
fileName2 = NULL;
if (!(file = fopen(fileName1->getCString(), "rb"))) {
fileName2 = fileName->copy();
fileName2->lowerCase();
if (!(file = fopen(fileName2->getCString(), "rb"))) {
fileName2->upperCase();
if (!(file = fopen(fileName2->getCString(), "rb"))) {
error(-1, "Couldn't open file '%s'", fileName->getCString());
delete fileName2;
errCode = errOpenFile;
return;
}
}
delete fileName2;
}
// create stream
obj.initNull();
str = new FileStream(file, 0, gFalse, 0, &obj);
ok = setup(ownerPassword, userPassword);
}

这里根据函数名可以大致推测出来相关功能 首先是检查了文件头 判断传入的是不是PDF文件 然后检查PDF文件的Xref表 检查文件是否损坏 然后检查加密情况 最后根据Xref交叉引用表 新建Catalog对象生成Catalog文档目录
c++// xpdf/PDFDoc.cc
GBool PDFDoc::setup(GString *ownerPassword, GString *userPassword) {
str->reset();
// check header
checkHeader();
// read xref table
xref = new XRef(str);
if (!xref->isOk()) {
error(-1, "Couldn't read xref table");
errCode = xref->getErrorCode();
return gFalse;
}
// check for encryption
if (!checkEncryption(ownerPassword, userPassword)) {
errCode = errEncrypted;
return gFalse;
}
// read catalog
catalog = new Catalog(xref);
if (!catalog->isOk()) {
error(-1, "Couldn't read page catalog");
errCode = errBadCatalog;
return gFalse;
}
...
}
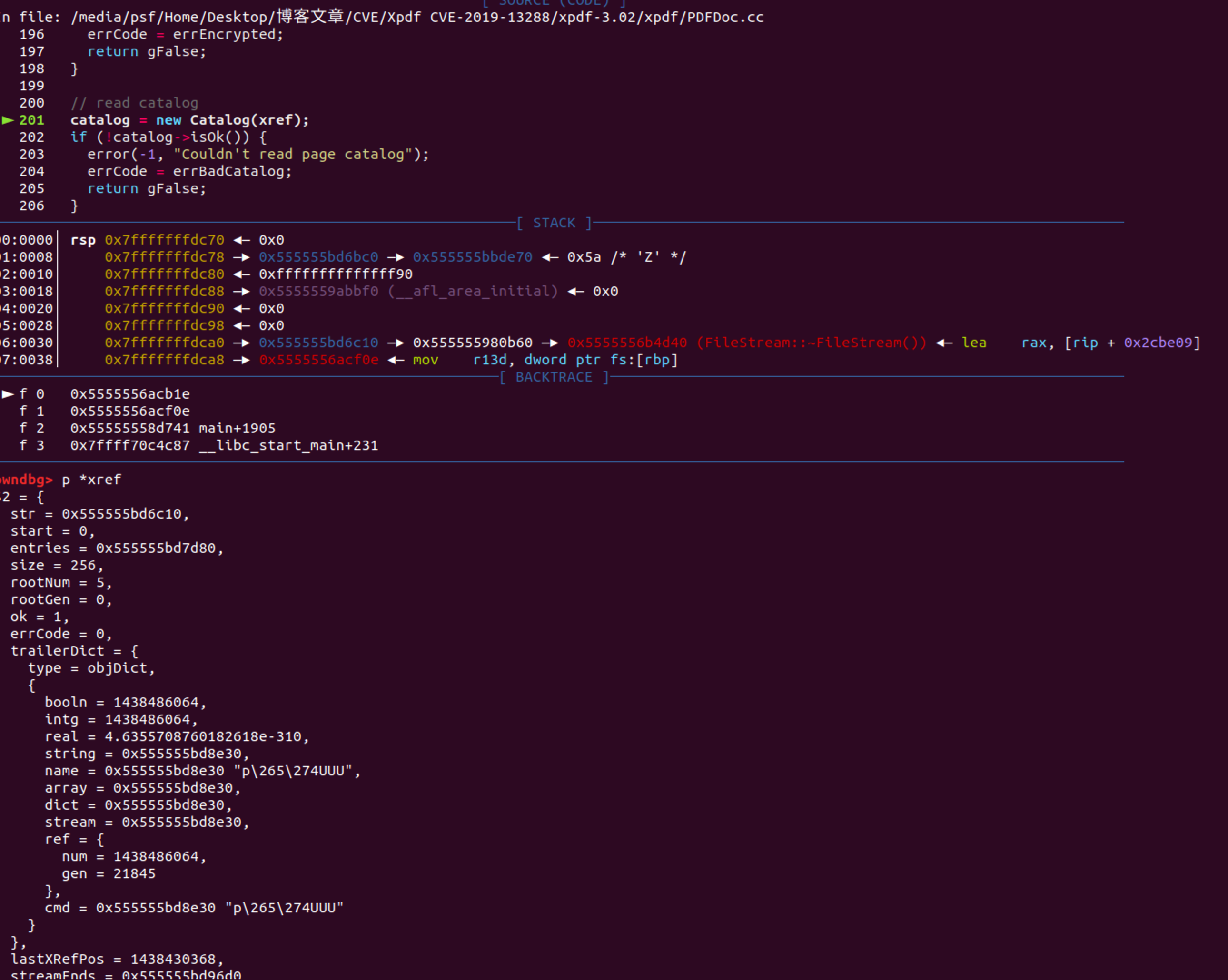
追入对象 发现上来就调用了getCatalog 未发现对catDict的赋值通过动态调试出catDict
c++// xpdf/Catalog.cc
Catalog::Catalog(XRef *xrefA) {
Object catDict, pagesDict, pagesDictRef;
Object obj, obj2;
char *alreadyRead;
int numPages0;
int i;
ok = gTrue;
xref = xrefA;
pages = NULL;
pageRefs = NULL;
numPages = pagesSize = 0;
baseURI = NULL;
xref->getCatalog(&catDict);
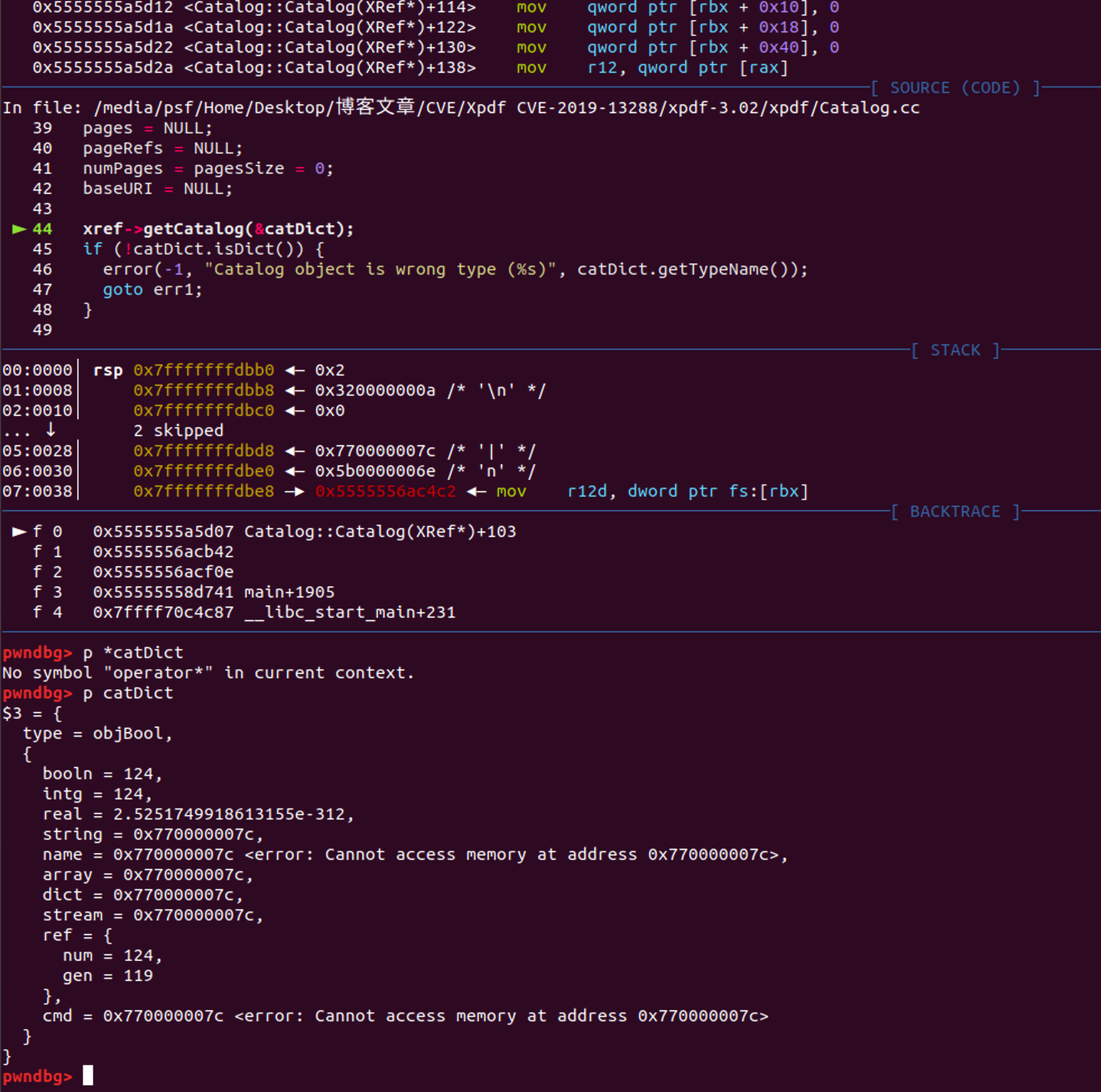
注意这里调用的是Object类型的fetch
c++ // xpdf/XRef.h
Object *getCatalog(Object *obj) { return fetch(rootNum, rootGen, obj); }
Object.fetch只是简单对xref.fetch进行封装 通过动调我们可以发现此时传入的参数为xref->fetch(5, 0, &catDict) 其中&catDict == 0x7fffffffdbd0
c++Object *Object::fetch(XRef *xref, Object *obj) {
return (type == objRef && xref) ?
xref->fetch(ref.num, ref.gen, obj) : copy(obj);
}
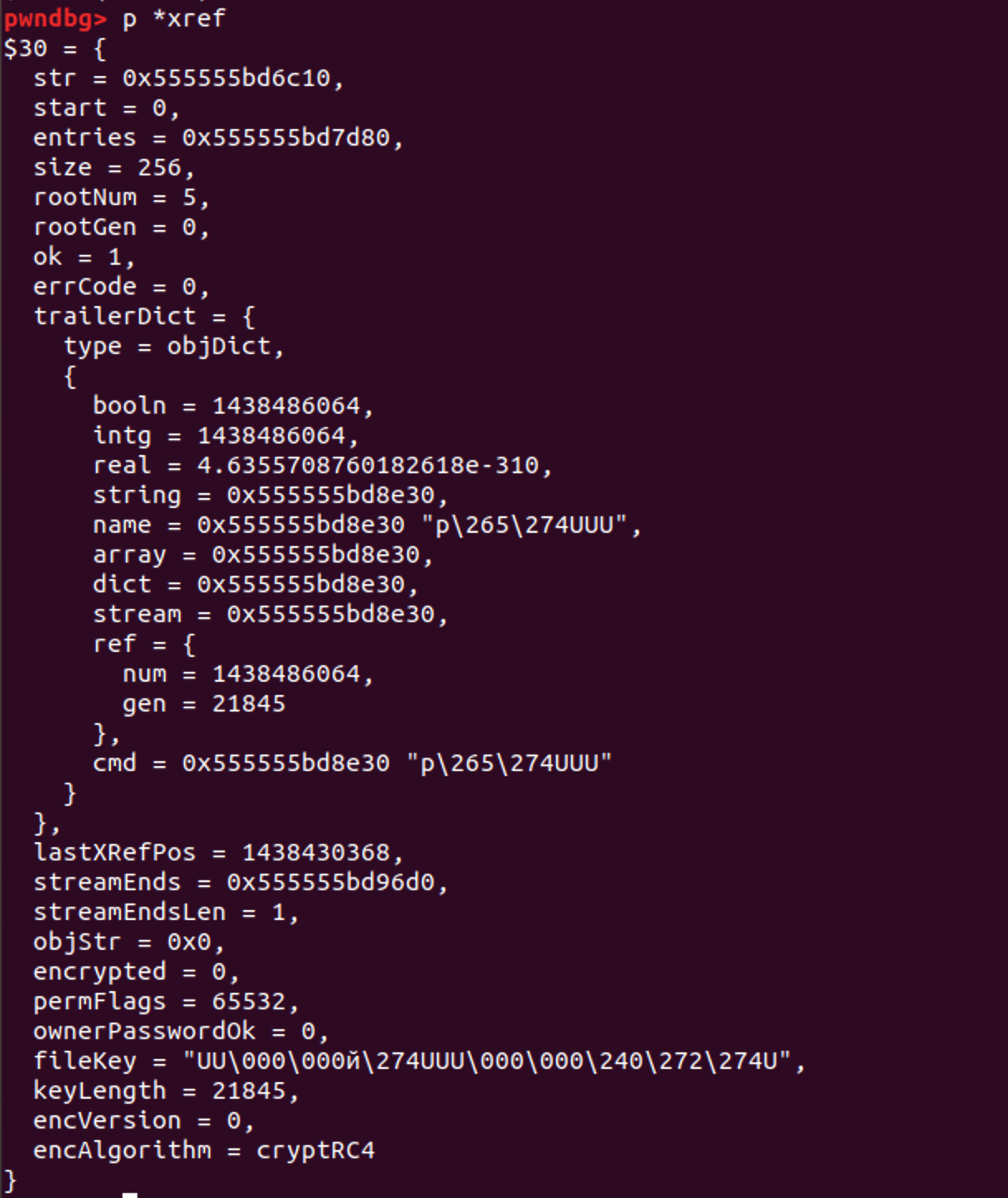
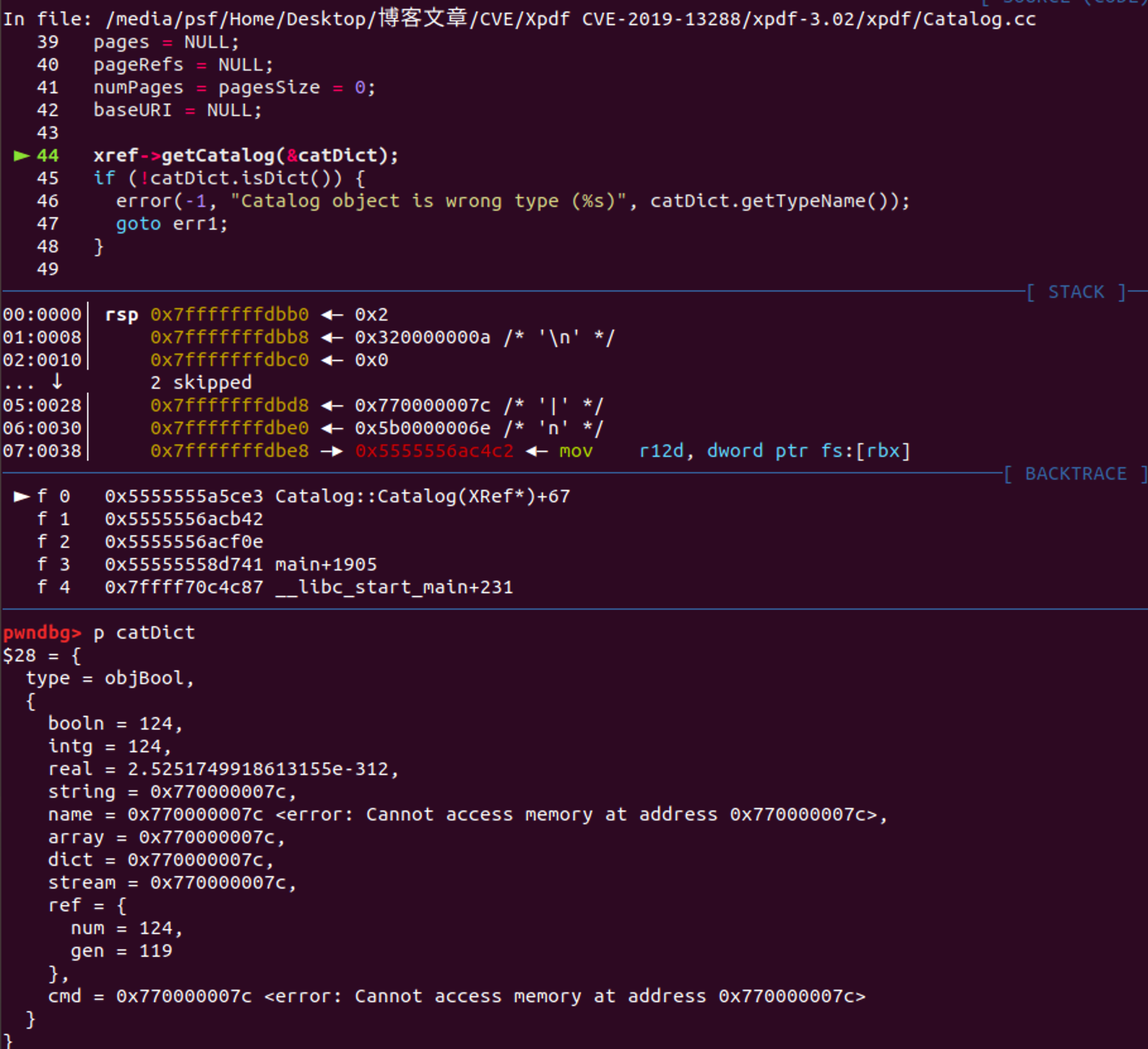
根据动态调试程序会流向XRef.cc:823 也就是parser->getObj 此时调用的参数为parser->getObj(&catDict, NULL, <RC4>, 21845, 5, 0)
c++// xpdf/XRef.cc
Object *XRef::fetch(int num, int gen, Object *obj) {
XRefEntry *e;
Parser *parser;
Object obj1, obj2, obj3;
// check for bogus ref - this can happen in corrupted PDF files
if (num < 0 || num >= size) {
goto err;
}
e = &entries[num];
switch (e->type) {
case xrefEntryUncompressed:
if (e->gen != gen) {
goto err;
}
...
parser->getObj(obj, encrypted ? fileKey : (Guchar *)NULL,
encAlgorithm, keyLength, num, gen); // here
...
}
根据栈帧显示 就是在此处的makeStream造成了无限递归 此时其参数为makeStream(&cataDict, NULL, <RC4>, 21845, 5, 0) 跟getObj的参数保持一致 注意此处的Dict对象是新建的
c++// xpdf/Parser.cc
Object *Parser::getObj(Object *obj, Guchar *fileKey,
CryptAlgorithm encAlgorithm, int keyLength,
int objNum, int objGen) {
char *key;
Stream *str;
Object obj2;
int num;
DecryptStream *decrypt;
GString *s, *s2;
int c;
...
obj->initDict(xref); // 此处新建Dict对象
while (!buf1.isCmd(">>") && !buf1.isEOF()) {
if (!buf1.isName()) {
error(getPos(), "Dictionary key must be a name object");
shift();
} else {
key = copyString(buf1.getName());
shift();
if (buf1.isEOF() || buf1.isError()) {
gfree(key);
break;
}
obj->dictAdd(key, getObj(&obj2, fileKey, encAlgorithm, keyLength,
objNum, objGen)); // Dict新增键值对
}
}
if (buf1.isEOF())
error(getPos(), "End of file inside dictionary");
// stream objects are not allowed inside content streams or
// object streams
if (allowStreams && buf2.isCmd("stream")) {
if ((str = makeStream(obj, fileKey, encAlgorithm, keyLength,
objNum, objGen))) {
...
此处调用dictLookup 并且调用dictLookup时的参数obj是新建的Object对象 所以与参数dict无关
c++// xpdf/Parser.cc
Stream *Parser::makeStream(Object *dict, Guchar *fileKey,
CryptAlgorithm encAlgorithm, int keyLength,
int objNum, int objGen) {
Object obj;
BaseStream *baseStr;
Stream *str;
Guint pos, endPos, length;
// get stream start position
lexer->skipToNextLine();
pos = lexer->getPos();
// get length
dict->dictLookup("Length", &obj);
if (obj.isInt()) {
length = (Guint)obj.getInt();
obj.free();
} else {
error(getPos(), "Bad 'Length' attribute in stream");
obj.free();
return NULL;
}
...
功能也比较明显 从Object对象的dict属性中调用lookup方法 其实就是从对象Object中寻找对应key的值
c++inline Object *Object::dictLookup(char *key, Object *obj)
{ return dict->lookup(key, obj); }
c++class Object {
public:
// Default constructor.
Object():
type(objNone) {}
// Initialize an object.
Object *initBool(GBool boolnA)
{ initObj(objBool); booln = boolnA; return this; }
Object *initInt(int intgA)
{ initObj(objInt); intg = intgA; return this; }
Object *initReal(double realA)
{ initObj(objReal); real = realA; return this; }
Object *initString(GString *stringA)
{ initObj(objString); string = stringA; return this; }
Object *initName(char *nameA)
{ initObj(objName); name = copyString(nameA); return this; }
Object *initNull()
{ initObj(objNull); return this; }
Object *initArray(XRef *xref);
Object *initDict(XRef *xref);
Object *initDict(Dict *dictA);
Object *initStream(Stream *streamA);
Object *initRef(int numA, int genA)
{ initObj(objRef); ref.num = numA; ref.gen = genA; return this; }
Object *initCmd(char *cmdA)
{ initObj(objCmd); cmd = copyString(cmdA); return this; }
Object *initError()
{ initObj(objError); return this; }
Object *initEOF()
{ initObj(objEOF); return this; }
// Copy an object.
Object *copy(Object *obj);
// If object is a Ref, fetch and return the referenced object.
// Otherwise, return a copy of the object.
Object *fetch(XRef *xref, Object *obj);
// Free object contents.
void free();
// Type checking.
ObjType getType() { return type; }
GBool isBool() { return type == objBool; }
GBool isInt() { return type == objInt; }
GBool isReal() { return type == objReal; }
GBool isNum() { return type == objInt || type == objReal; }
GBool isString() { return type == objString; }
GBool isName() { return type == objName; }
GBool isNull() { return type == objNull; }
GBool isArray() { return type == objArray; }
GBool isDict() { return type == objDict; }
GBool isStream() { return type == objStream; }
GBool isRef() { return type == objRef; }
GBool isCmd() { return type == objCmd; }
GBool isError() { return type == objError; }
GBool isEOF() { return type == objEOF; }
GBool isNone() { return type == objNone; }
// Special type checking.
GBool isName(char *nameA)
{ return type == objName && !strcmp(name, nameA); }
GBool isDict(char *dictType);
GBool isStream(char *dictType);
GBool isCmd(char *cmdA)
{ return type == objCmd && !strcmp(cmd, cmdA); }
// Accessors. NB: these assume object is of correct type.
GBool getBool() { return booln; }
int getInt() { return intg; }
double getReal() { return real; }
double getNum() { return type == objInt ? (double)intg : real; }
GString *getString() { return string; }
char *getName() { return name; }
Array *getArray() { return array; }
Dict *getDict() { return dict; }
Stream *getStream() { return stream; }
Ref getRef() { return ref; }
int getRefNum() { return ref.num; }
int getRefGen() { return ref.gen; }
char *getCmd() { return cmd; }
// Array accessors.
int arrayGetLength();
void arrayAdd(Object *elem);
Object *arrayGet(int i, Object *obj);
Object *arrayGetNF(int i, Object *obj);
// Dict accessors.
int dictGetLength();
void dictAdd(char *key, Object *val);
GBool dictIs(char *dictType);
Object *dictLookup(char *key, Object *obj);
Object *dictLookupNF(char *key, Object *obj);
char *dictGetKey(int i);
Object *dictGetVal(int i, Object *obj);
Object *dictGetValNF(int i, Object *obj);
// Stream accessors.
GBool streamIs(char *dictType);
void streamReset();
void streamClose();
int streamGetChar();
int streamLookChar();
char *streamGetLine(char *buf, int size);
Guint streamGetPos();
void streamSetPos(Guint pos, int dir = 0);
Dict *streamGetDict();
// Output.
char *getTypeName();
void print(FILE *f = stdout);
// Memory testing.
static void memCheck(FILE *f);
private:
ObjType type; // object type
union { // value for each type:
GBool booln; // boolean
int intg; // integer
double real; // real
GString *string; // string
char *name; // name
Array *array; // array
Dict *dict; // dictionary
Stream *stream; // stream
Ref ref; // indirect reference
char *cmd; // command
};
};
可以看到跟预测的功能差不多
c++Object *Dict::lookup(char *key, Object *obj) {
DictEntry *e;
return (e = find(key)) ? e->val.fetch(xref, obj) : obj->initNull();
}
这里比较关键的就是 动态跟进find 发现e->val类型为objRef
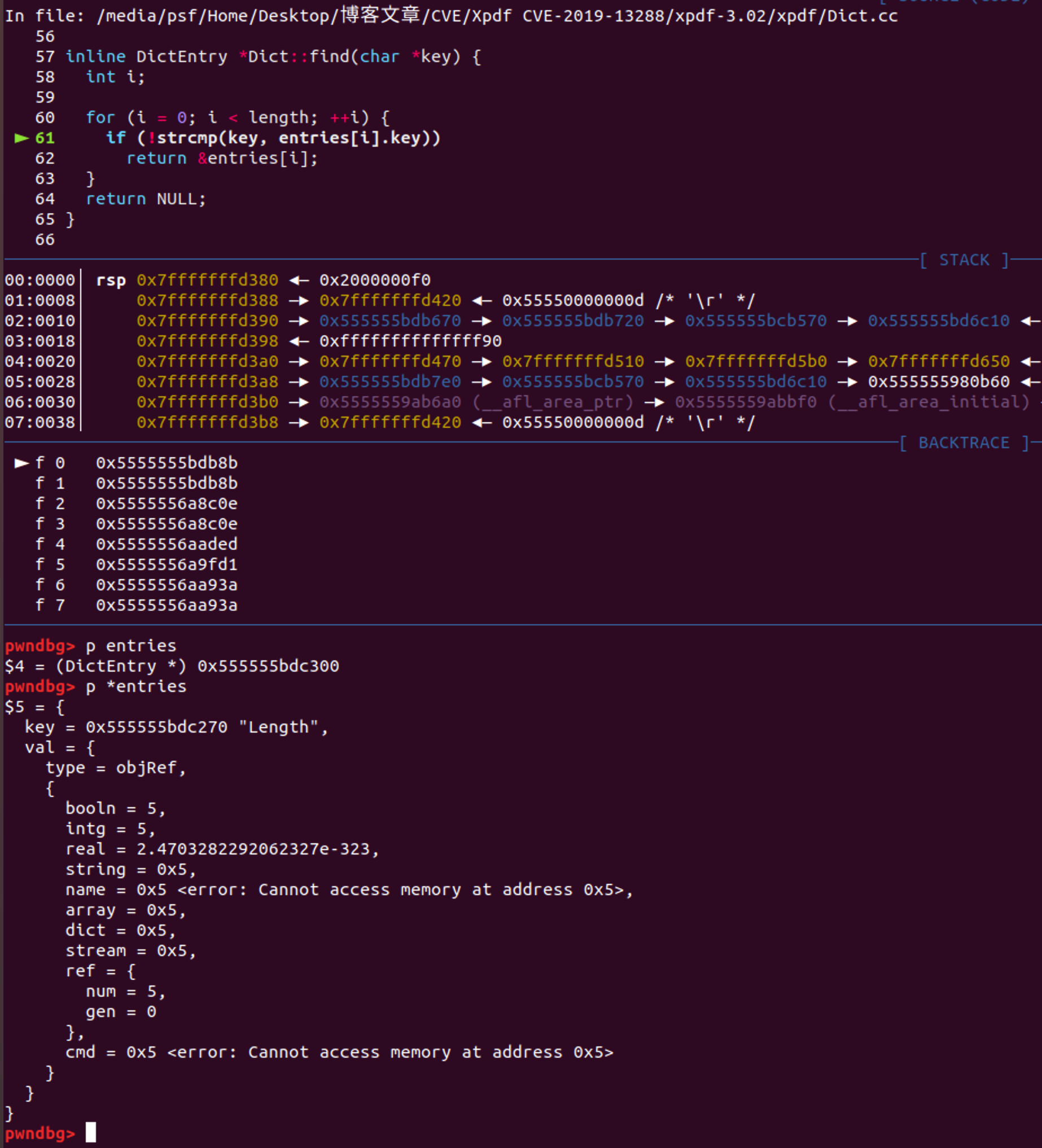
其中由于上面看到的e->val->type == objRef 所以满足条件 执行xref->fetch(5, 0, newobj) 至此陷入无限递归
c++Object *Object::fetch(XRef *xref, Object *obj) {
return (type == objRef && xref) ?
xref->fetch(ref.num, ref.gen, obj) : copy(obj);
}
整体修复思路也比较简单 要么限制递归次数 要么对寻找出来的e的类型进行校验即可
本文作者:Du4t
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!